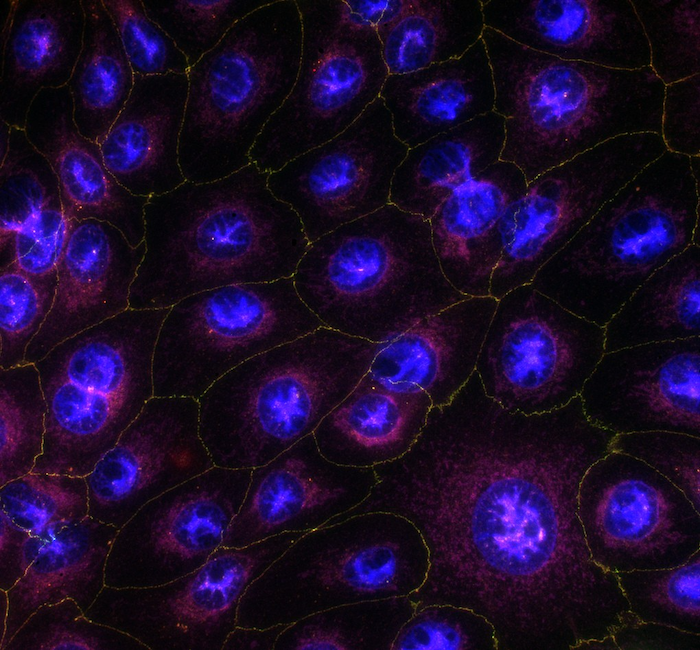
Permeability
In vitro permeability
Cornea and outer blood-retinal barrier formed by the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) pose a challenge for novel chemical entities and biomolecules to enter the eye. Assessing the ability of novel molecules to bypass these barriers should be conducted early in the drug development process.
Cornea
Experimentica offers in vitro permeability testing services using human-derived corneal epithelial cells. Utilizing the HCE-T1 cells (Riken, Japan), this in vitro model effectively mimics the human cornea’s tightness and cellular architecture, allowing evaluating novel molecule’s ability to enter the eye by transcorneal route2-4.
In collaboration with Finnadvance, we have also developed an advanced human cornea organ-on-a-chip model using the AKITA® platform5. This state-of-the-art microfluidic platform reduces the time to study initiation from six to three weeks. Combined with lower test article requirements, it enables faster, more cost-efficient permeability profiling in early-stage ocular drug development.
Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
The RPE forms a tight monolayer between the retina and the choroidal blood vessels, limiting the entry of molecules into the retina following systemic administration. RPE cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (PCi-RPE6, Phenocell, France) exhibit the key phenotypic and functional characteristics of primary human RPE7 cells, providing a reliable in vitro model for studying novel molecules transport across the outer blood-retinal barrier.

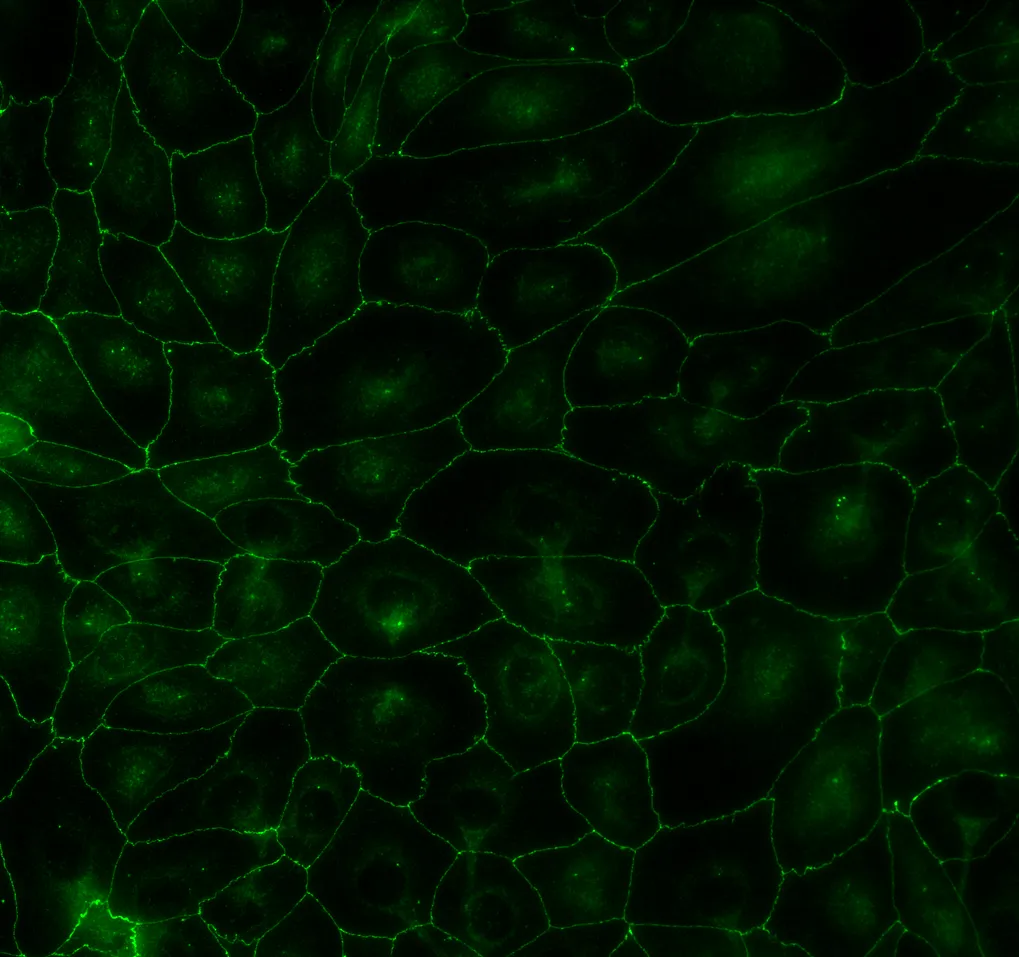
Technical details
– Human corneal epithelial cells (HCE-T, RIKEN, Japan)
– Human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived retinal pigmented epithelial cells (PCi-RPE, Phenocell, France)
– Transwell-12 culture inserts (Corning, NY, USA)
– AKITA® Plate96-Single microfluidic platform (Finnadvance Ltd, Helsinki, Finland)
– 6-carboxyfluorescein
– Rhodamine B
– FITC-dextran 4 000 Da
– FITC-dextran 70 000 Da
The apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) value
Highlights of this model
Corneal permeability
Cornea: key barrier in topical ocular drug delivery, HCE-T cells mimic cornea’s tight junctions and cellular structure
RPE permeability
iPSC-RPE: form tight junctions and polarized monolayers, effectively mimicking the outer blood-retinal barrier
Tight barriers
Tight barriers mimic physiological conditions. Accurate permeability measurements in HCE-T and iPSC-RPE models help distinguish between transcellular and paracellular transport which is essential for understanding how the drug moves through the barriers
References
- Araki-Sasaki K, Ohashi Y, Sasabe T, Hayashi K, Watanabe H, Tano Y, Handa H. An SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line and its characterization. IOVS 1995,36:614–621.
- Toropainen et al. Culture model of human corneal epithelium for prediction of ocular drug absorption. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2001,42(12):2942-2948.
- Reichl. Cell culture models of the human cornea – a comparative evaluation of their usefulness to determine ocular drug absorption in-vitro. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008;60(3):299-307.
- Žiniauskaitė A, Cėpla V, Jelinskas T, Eimont R, Ulčinas A, Aldonytė R, Valiokas R, Kalesnykas G, Hakkarainen JJ. Introducing an Efficient In Vitro Cornea Mimetic Model for Testing Drug Permeability. Sci. 2021; 3(3):30.
- Litvinaviciute D, Vergun O, Nguyen TH, Mosser S, Hakkarainen JJ. Human cornea-on-a-chip – opportunities and challenges. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science June 2025, Vol.66, 2301.
- Maruotti J, Wahlin K, Gorrell D, Bhutto I, Lutty G, Zack DJ. A simple and scalable process for the differentiation of retinal pigment epithelium from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013,2(5):341-354.
- Hakkarainen JJ, Maruotti J, Seppänen A, Onteniente B, Kalesnykas G, Reinisalo M. hiPSC-derived RPE cells: Characterization of blood-retinal barrier properties and drug permeability. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science September 2016, Vol.57, 268
We are here to help
Whether you have a question about our preclinical models, capabilities, pricing or anything else, our team is ready to answer all your inquiries.
Related services
Desiccating Stress + Scopolamine-Induced Dry Eye
A mouse dry eye model using desiccating stress and pharmacologic inhibition mimics key features of human DED, supporting therapy evaluation through imaging and histological analysis.
Learn moreRT-qPCR
qPCR measures gene expression in ocular tissues, supporting disease research and treatment evaluation.
Learn moreELISA
ELISA enables sensitive protein detection and quantification in ocular tissues and biofluids.
Learn moreWestern Blotting
Western blot detects protein expression and modifications in ocular tissues with high sensitivity and precision
Learn moreHistological staining
Histological staining techniques for ocular and nervous system tissues to support detailed analysis.
Learn moreCheck out our latest news and activities
All News