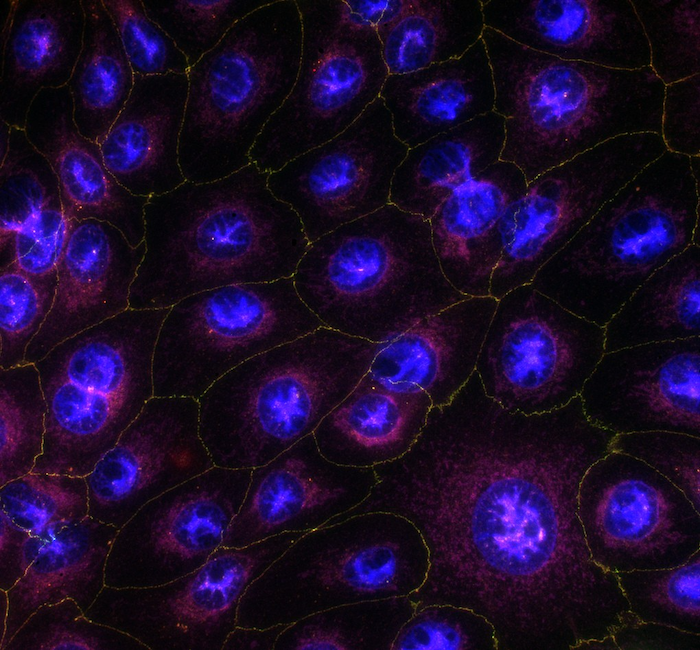
In vitro models
Toxicity – in vitro
In vitro cell-based cytotoxicity assays are useful during the early phase of drug development. These assays allow evaluation of both acute and chronic effects of test compounds.
Cornea
Human corneal epithelial cells (HCE-T1, RIKEN, Japan) are typically used for evaluation of novel chemical entities’ or topical formulations’ cytotoxic effects. The cells can be exposed to test articles for a period of a few minutes to 3-4 days. Benzalkonium chloride (BAC), which is a typical preservative in multi-dose ophthalmic solutions, is used as positive control for HCE-T cells2.
Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
RPE cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (PCi-RPE3, Phenocell, France) introduce the key phenotypic and functional characteristics of primary human RPE cells4. This in vitro cell model can be used reliably to screen test articles cytotoxic effects.
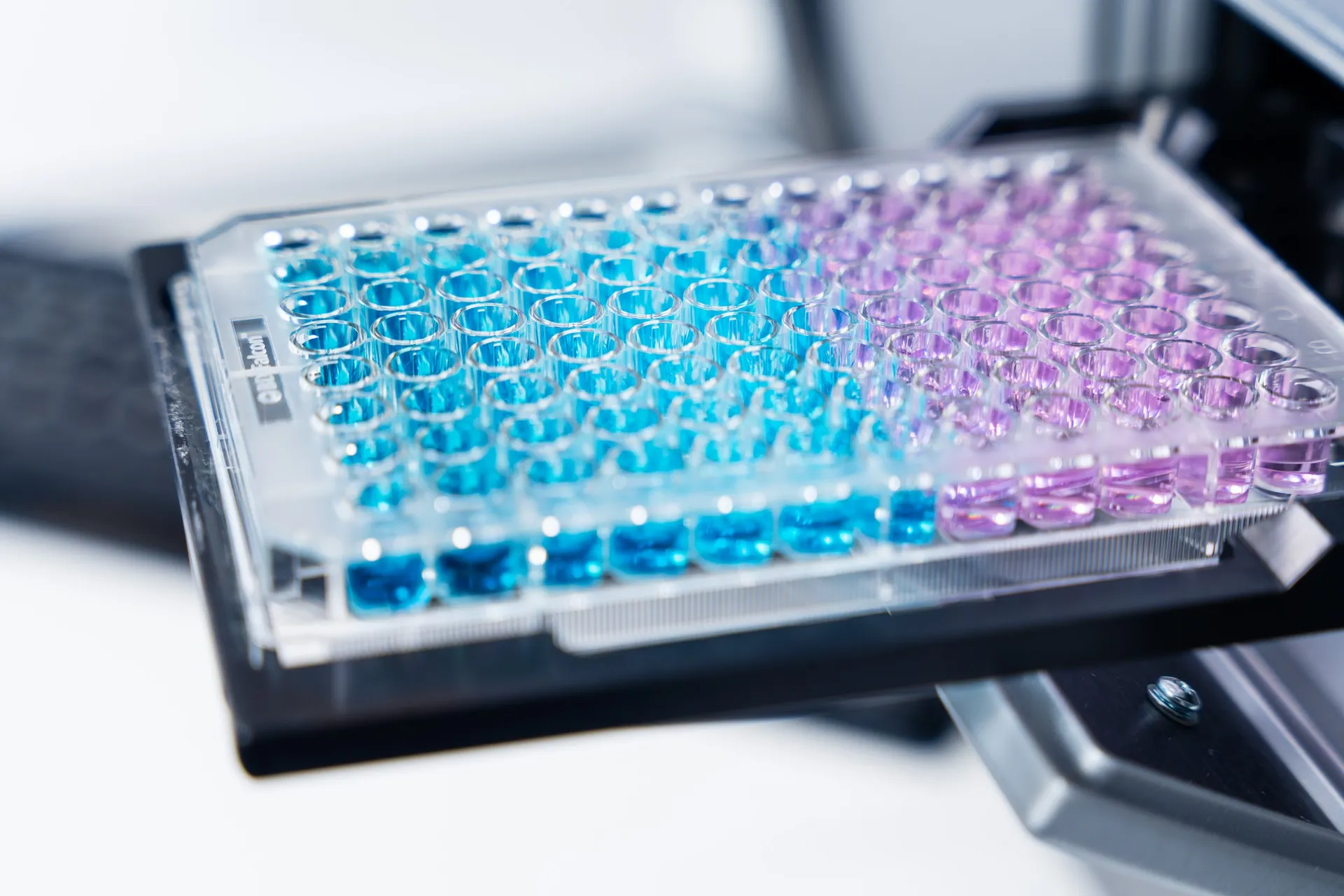

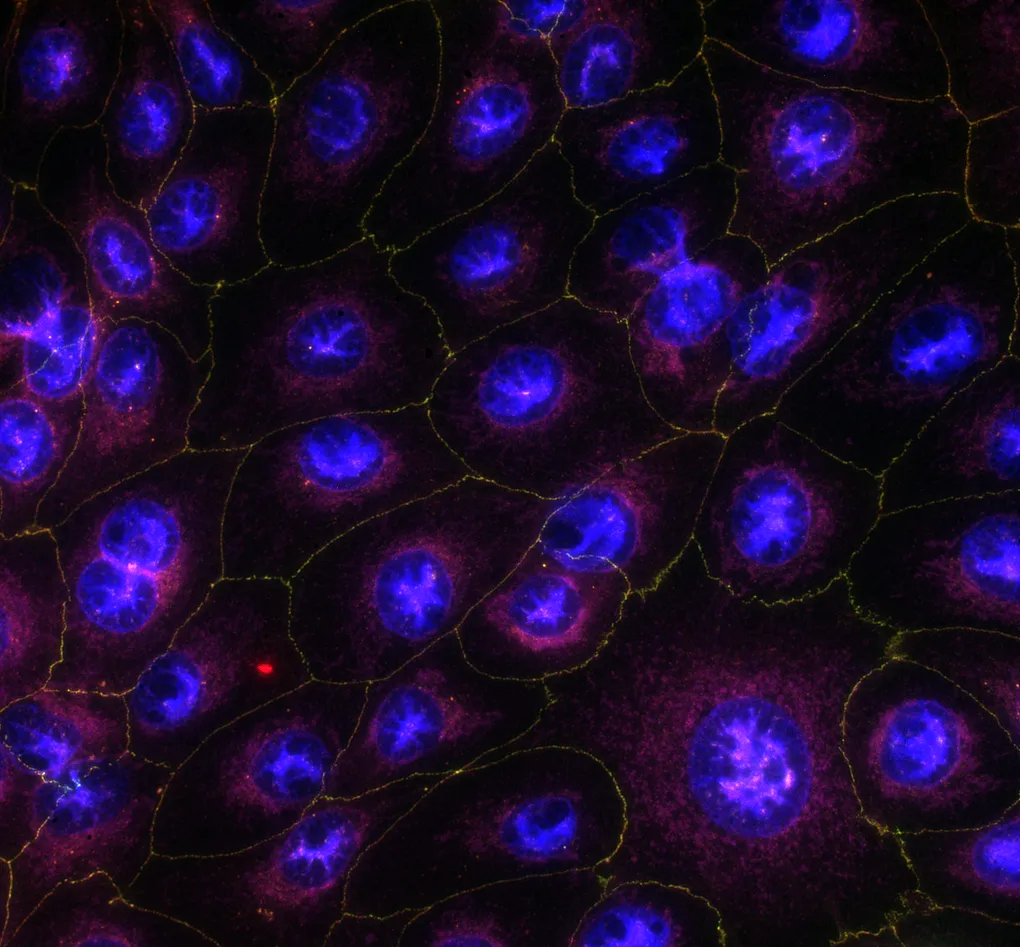
Technical details
- Human corneal epithelial cells (HCE-T, RIKEN, Japan)
- Human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived retinal pigmented epithelial cells (PCi-RPE, Phenocell, France)
- Resazurin cell viability assay
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay
Cell viability
Highlights of this model
Easy and cost-efficient assessment of test article-induced cytotoxicity
Screening of several test articles or concentrations at the same time
Combined use of various cytotoxic insults
References
- Araki-Sasaki K, Ohashi Y, Sasabe T, Hayashi K, Watanabe H, Tano Y, Handa H. An SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line and its characterization. IOVS 1995,36:614–621. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7534282/
- Hakkarainen JJ, Reinisalo M, Ragauskas S, Seppänen A, Kaja S, Kalesnykas G. Acute cytotoxic effects of marketed ophthalmic formulations on human corneal epithelial cells. Int J Pharm. 2016;511(1):73-78. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27374205/
- Maruotti J, Wahlin K, Gorrell D, Bhutto I, Lutty G, Zack DJ. A simple and scalable process for the differentiation of retinal pigment epithelium from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013,2(5):341-354. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23585288/
- Hakkarainen JJ, Maruotti J, Seppänen A, Onteniente B, Kalesnykas G, Reinisalo M. hiPSC-derived RPE cells: Characterization of blood-retinal barrier properties and drug permeability. ARVO2016 Poster. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science September 2016, Vol.57, 268.
https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2559157
We are here to help
Whether you have a question about our preclinical models, capabilities, pricing or anything else, our team is ready to answer all your inquiries.
Related services
Massa metus risus euismod elit leo nisi suscipit
vulputate velit. Vel ac volutpat adipiscing vitae.
Tissue processing
Specialized processing of ocular and neural tissues employing methods such as flat mounting, paraffin and cryo embedding, and precision sectioning.
Learn moreImmunohistochemistry
Experimentica offers a wide range of single and multiplex immunofluorescence labeling to explore disease pathogenesis and therapeutic targets.
Learn moreHistological staining
Histological staining techniques for ocular and nervous system tissues to support detailed analysis.
Learn moreELISA
ELISA enables sensitive protein detection and quantification in ocular tissues and biofluids.
Learn moreRT-qPCR
qPCR measures gene expression in ocular tissues, supporting disease research and treatment evaluation.
Learn moreWestern Blotting
Western blot detects protein expression and modifications in ocular tissues with high sensitivity and precision
Learn moreCheck out our latest news and activities
All News