Comprehensive characterization of the rat magnetic microbead model
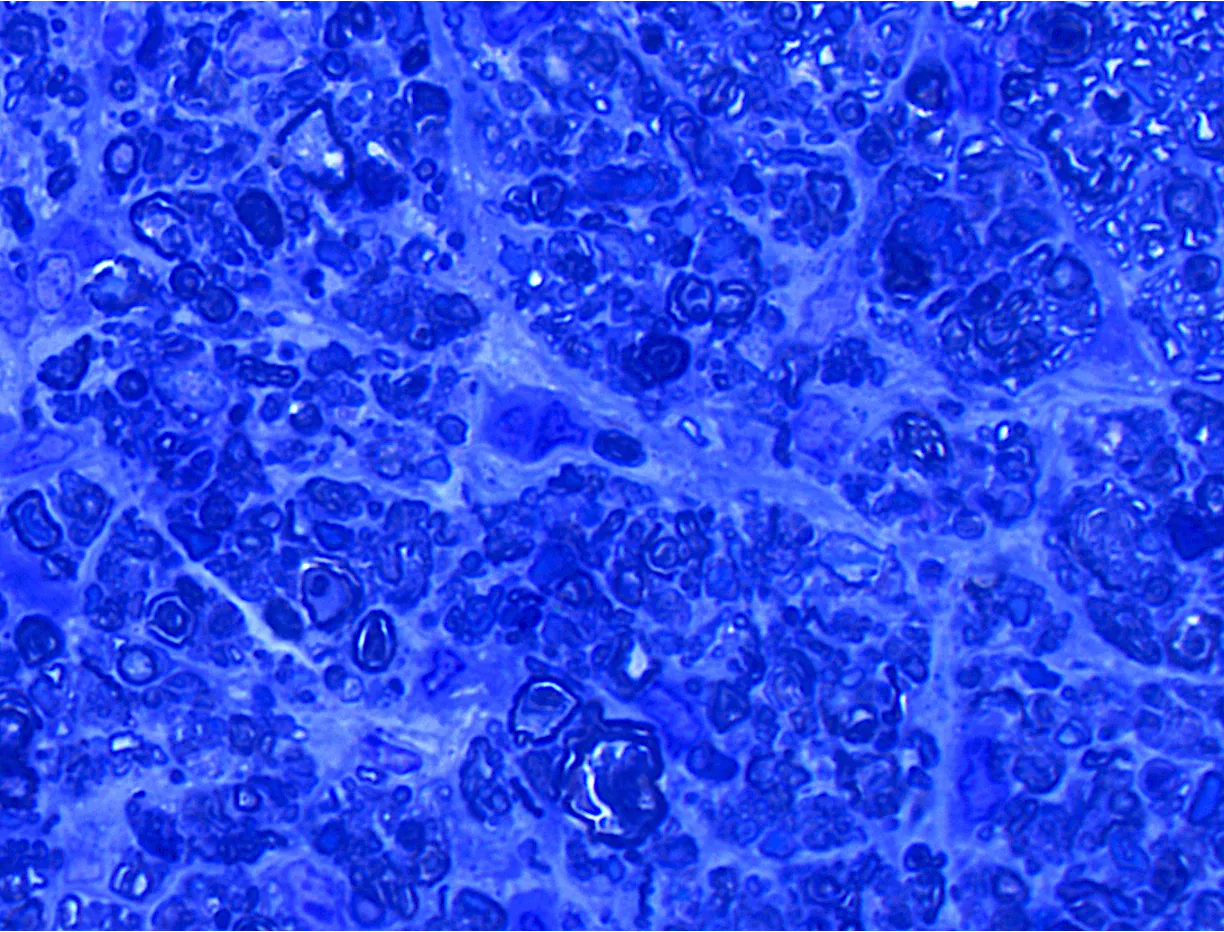
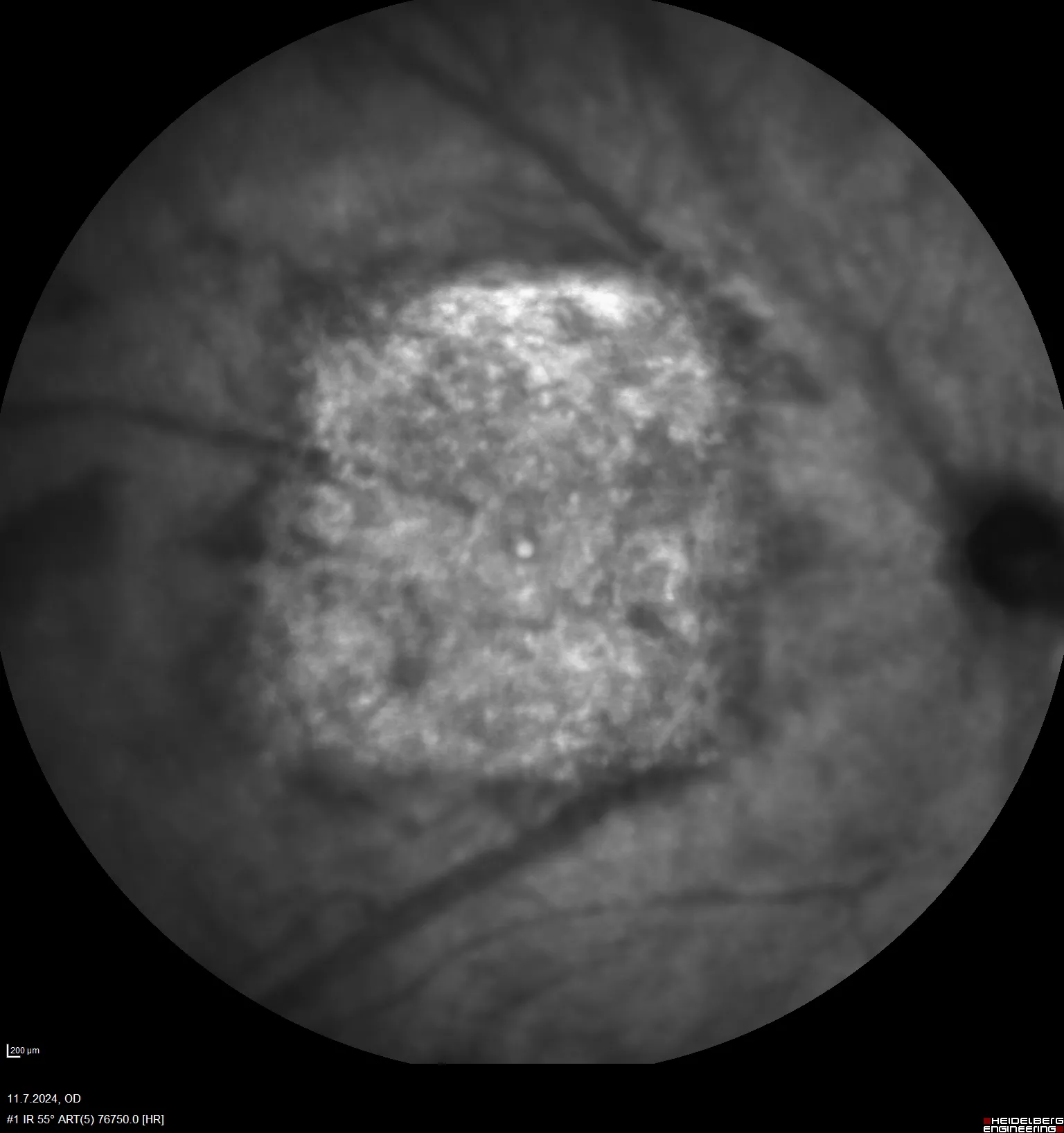
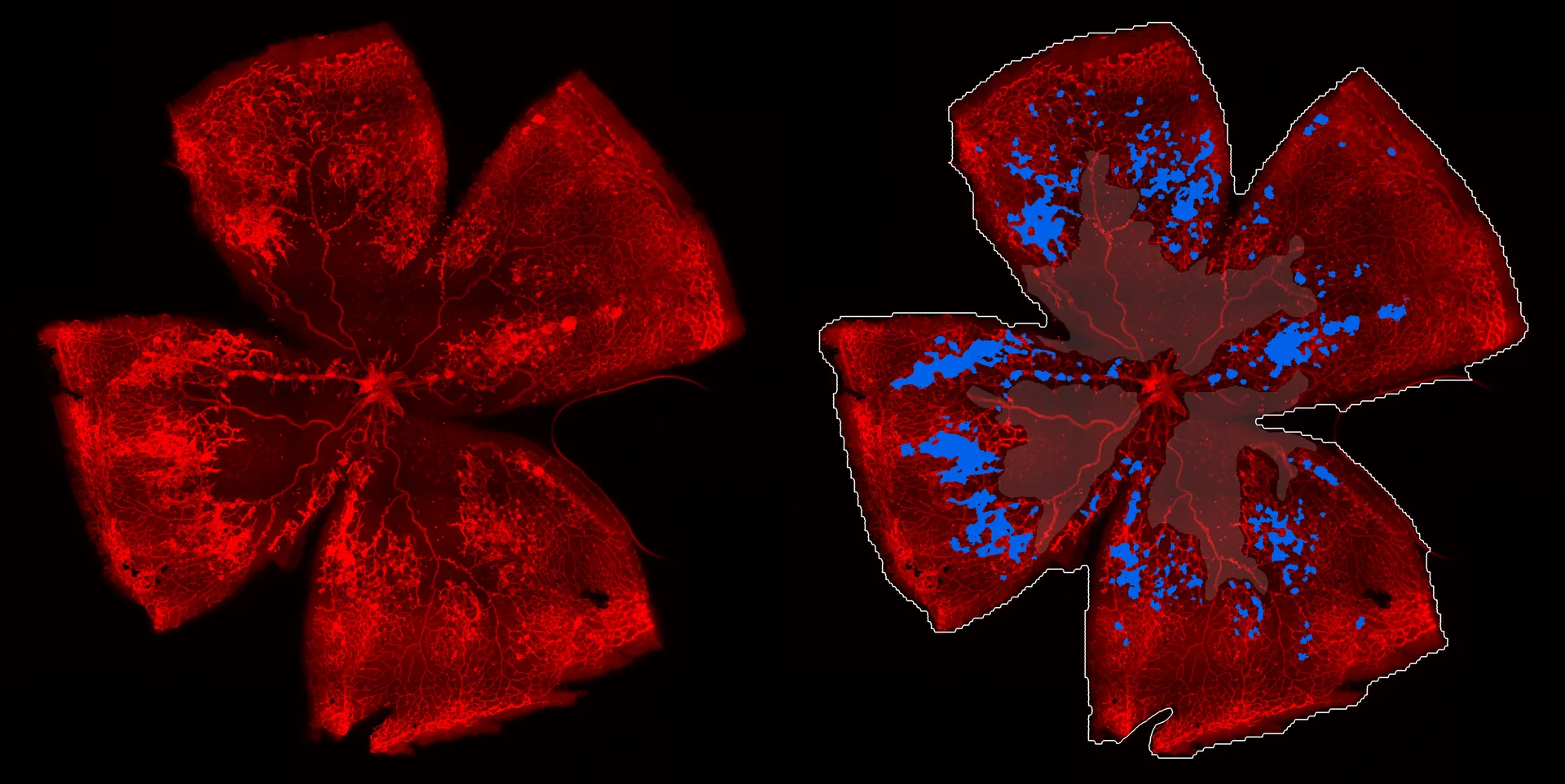
Glaucoma is a leading cause of irreversible blindness, highlighting the urgent need for reliable preclinical models that capture both structural and functional disease aspects. Our recently published study by Kernius Mickevičius provides a longitudinal evaluation of the rat magnetic microbead model of ocular hypertension by combining multimodal monitoring tools including spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT), pattern electroretinography (pERG), optomotor testing, and morphological analysis.
Learn more