Summary: Experimentica is pleased to announce its participation in the annual meeting of the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2023.

Content
Experimentica attends ARVO 2023 – follow our Scientists and visit us at booth #1428!
The ARVO meeting is a leading global event in the field of eye and vision research, bringing together researchers, clinicians, and industry professionals to present and discuss the latest scientific advancements and technologies in vision research.
At the 2023 ARVO meeting in New Orleans, La. (April 23 – 27), Experimentica will be showcasing its innovative preclinical contract research services for ophthalmic drug discovery and development.
With a decade of experience in the field of ophthalmology, Experimentica provides a wide range of in vivo and in vitro services, including pharmacology and efficacy studies, PK studies, and safety and toxicology studies.
Our team of experts will be on hand to discuss how our services can help accelerate your research and bring new therapies to patients with ocular diseases such as but not limited to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma.
We look forward to connecting with fellow researchers and industry professionals at the ARVO meeting this year and sharing our latest scientific insights and capabilities in ophthalmic research.
Presented by Experimentica Ltd.
Do not miss out on our team’s abstracts in physiopathology and preclinical model development.
A B S T R A C T
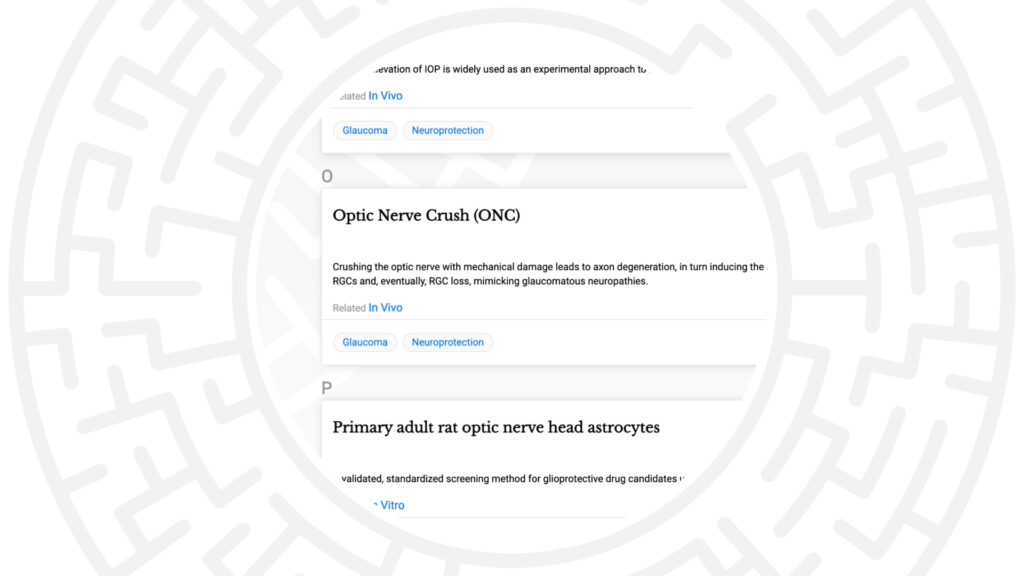
Optomotor reflex in the mouse optic nerve crush model for glaucomatous optic neuropathies.
Animal Models | 2:15 PM – 4:15 PM CDT on Wednesday, April 26 | C0240
Authors: Vähätupa M, Tenhunen A, Tähtivaara L, Jääskeläinen N, Partanen P, Kolehmainen A, Lappeteläinen B, Koskenniemi H, Mertano P, Jokinen V, Kvietkauskiene N, Bijeikis S, Jarutis J, Kalesnykas G, Cerrada-Gimenez M, Kaja S
Purpose: Experimental optic nerve crush (ONC) in rodents has been widely used as a model for traumatic optic nerve injury, glaucomatous optic neuropathy, and, more generally, retinal ganglion cell (RGC) damage. The purpose of this Study was to evaluate the structure-function relationships in the mouse ONC, focusing on the longitudinal in-life assessment of visual function by pattern electroretinography (PERG) and optomotor reflex (OMR), and retinal structure by spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT).
A B S T R A C T
Differential effects of E. coli versus S. typhimurium derived lipopolysaccharides on development of uveitis in the rabbit.
Pathobiology of Microbial Infections | 8:00 AM – 10:00 AM CDT on Sunday, April 23 | C0186
Authors: Bacellar-Galdino M, Pappenhagen NE, Kaja S
Purpose: Uveitis describes the inflammation of the uveal tissues of the eye. Posterior uveitis, the inflammation of the choroid, can affect the retina and optic nerve and result in blindness. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is routinely used to induce a phenotype of infectious uveitis in rabbits. However, descriptions of the LPS-induced uveitis models differ greatly in the literature. The purpose of this study was to standardize the LPS-induced model for infectious uveitis in pigmented Dutch Belted rabbits using LPS derived from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium.
A B S T R A C T
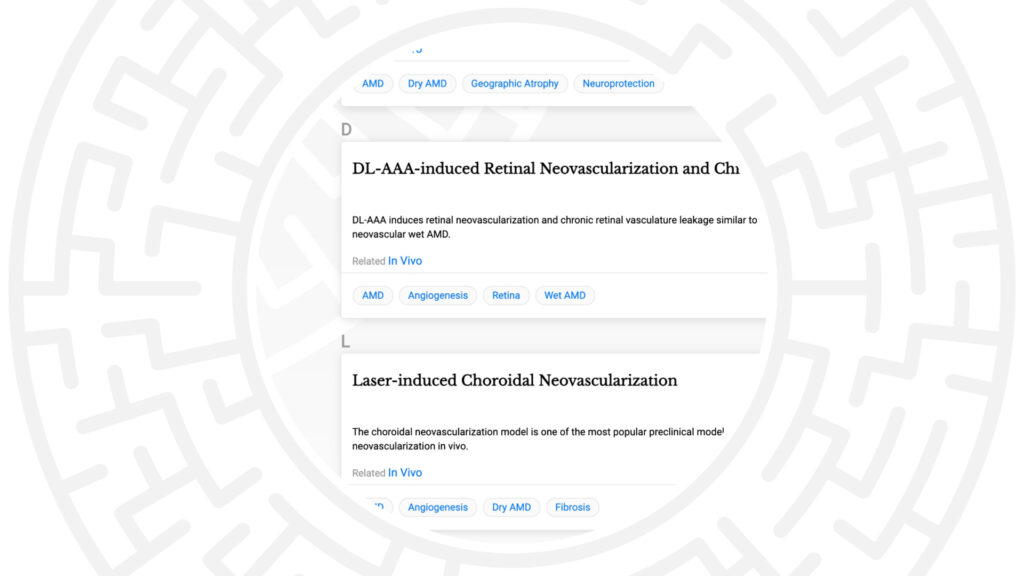
Involvement of thioredoxin system in laser-induced CNV mouse model.
AMD translational studies | 8:45 AM – 10:30 AM CDT on Tuesday, April 25 | C0014
Authors: Cesna R, Litvinaviciute D, Urbanaviciute J, Lelyte I, Mickevicius K, Adamoniene O, Neverauskas D, Ragauskas S, Kalesnykas G, Ghosh AK, Kaja S
Purpose: Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) plays important role in cellular redox-state homeostasis by binding and inhibiting thioredoxin. Cellular redox homeostasis controlled by thioredoxin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression. The objective of this Study was to evaluate expression of key genes of the thioredoxin-VEGF pathway (thioredoxin-1, TXN1; TXNIP; hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A; vascular endothelial growth factor A, VEGFA) in the mouse laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) model.
A B S T R A C T
Environmental particulate matter of different sizes leads to differential damage of the ocular surface.
Immunobiology of Eye Disease: The Ocular Microenvironment | 3:15 PM – 5:15 PM CDT on Monday, April 24 | B0382
Authors: Ghosh AK, Iqbal S, Pappenhagen NE, Bacellar-Galdino M, Kaja S, Rao VR
Purpose: Environmental particulate matter (PM) is a known trigger for development of ocular surface disease. The purpose of this study was to compare the toxic effects of small and large PM in rabbit corneal epithelial cells (SIRC) in vitro and ocular surface damage in rabbits in vivo.
A B S T R A C T
AAV-mediated expression of human VEGF-A as a novel rat model of diabetic retinopathy.
Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Retinopathy | 11:30 AM – 1:15 PM CDT on Monday, April 24 | C0313
Authors: Lelyte I, Ragauskas S, Paulauskas T, Ahmed Z, Kaja S, Kalesnykas G
Purpose: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a complex disease displaying a complex angiogenic pathology, including upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF), vascular leakage and neovascularization, ultimately leading to visual impairment. However, animal models accurately reflecting vascular pathologies of DR are lacking. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated long-term expression of VEGF to establish angiogenic DR-related phenotypes in Brown Norway rats.
A B S T R A C T
Efficacy of topical ketotifen and prednisolone in the rabbit 48/80 model for allergic conjunctivitis.
Advances in Ocular Inflammatory Disease Therapy | 3:30 PM – 5:15 PM CDT on Tuesday, April 25 | B0390
Authors: Pappenhagen NE, Iqbal S, Kaja S, Jamison JA, Bacellar-Galdino M
Purpose: Allergic conjunctivitis is a common allergic disease that affects the cornea, conjunctiva, and lids of the eye. The purpose of this study was to determine the efficacy of the histamine H1 receptor blocker, ketotifen (0.035%) and the glucocorticoid, prednisolone (1%) in the New Zealand White (NZW) rabbit compound 48/80 model for allergic conjunctivitis.
A B S T R A C T
Aflibercept exerts structural protection against diabetic retinopathy – associated inner retinal abnormalities in the mouse STZ model.
Diabetic Retinopathy (clinical studies) | 12:00 PM – 1:45 PM CDT on Sunday, April 23 | B0009
Authors: Ragauskas S, Paulauskas T, Lelyte l, Neverauskas D, Mickevicius K, Cesna R, Kalesnykas G, Kaja S
Purpose: Streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic retinopathy (DR) in rodents is widely used model for drug discovery for novel anti-angiogenic agents targeting DR-associated phenotypes. The purpose of this study was to investigate the pharmacological effects of Aflibercept (Eylea®) in the mouse STZ model.
A B S T R A C T
Recombinant human PRG4 alleviates signs of allergic conjunctivitis in vivo.
Time and location to be announced
Authors: Iqbal S, De Alba M, Sagalov A, Hariani HN, Pappenhagen N, Ghosh AK, Rao VR, Fareed J, Bacellar-Galdino M, Kaja S
Purpose: Allergic conjunctivitis (AC) is a multifactorial disease associated with redness and swelling of the conjunctiva, increased lacrimation, and severe itching. Management includes lubricants, topical corticosteroids, NSAIDs, and antihistamines. Limited efficacy and drug-induced adverse reactions call for novel safer and more efficacious treatments. Lubricin/PRG4 is an endogenous proteoglycan that has emerged as a key natural molecule in the lubrication of the ocular surface. Compound 48/80 (C48/80) promotes mast cell degranulation and topical instillation of C48/80 is a well-established model for AC in rabbits. The purpose of this study was to investigate the efficacy of PRG4 in models for C48/80-induced AC.
A B S T R A C T
Subconjunctival administration of Aflibercept protects against neovascularization in the mouse CNV model.
AMD anti-VEGF | 3:15 PM – 5:00 PM CDT on Monday, April 24 | C0186
Authors: Cerrada-Gimenez M, Vähätupa M, Lappeteläinen B, Tähtivaara L, Jokinen V, Haapaniemi A M, Vergun O, Kvietkauskiene N, Bijeikis S, Jarutis J, Kolehmainen A, Mertano P, Sarkola E, Kalesnykas G, Kaja S
Purpose: Anti-VEGF treatments have shown effectivity in limiting the progression of the neovascular lesions and improved disease outcome in the CNV model. Aflibercept has been approved since 2011 as treatment against AMD. Aflibercept is administered intravitreally every two months. In the current study we compared the efficacy of Aflibercept administered intravitreally and subconjuctivally in the mouse CNV model.
Presented by Experimentica Ltd. collaborators
A B S T R A C T
An Investigation of Dark-adapted Electroretinogram (ERG) Suppression in the Rabbit: Role of an Excipient or a Species-related Sensitivity?
Authors: Brock W, Kocab A J, Jamison JA, Bacellar-Galdino M, Zacks DN
Purpose: Suppression of the dark-adapted electroretinogram (ERG) was observed in Dutch-belted (DB) rabbits following intravitreal (IVT) injection of a small peptide (MW <5kDa) formulated with poloxamer 407 (PX407). Similar changes were not observed in mini pigs (MP). Since ERG suppression of the dark-adapted b-wave without an effect on the a-wave is unusual, studies were carried out to investigate this finding in rabbits.
A B S T R A C T
Overexpression of endothelin-1 elicits phenotypes of reactive astrocytosis and elastinopathy in primary optic nerve astrocytes.
Authors: Kaja S, Ghosh AK, Floss J, Root B, Betancourt-Szymanowska C, Rao VR
Purpose: Elevated levels of the vasoactive peptide endothelin-1 (ET-1) are associated with the pathophysiology of various subtypes of glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Here we sought to investigate the effects of ET-1 overexpression in primary optic nerve head astrocytes (ONHA).
A B S T R A C T
Quantification of clinically-relevant biomarkers in primary human trabecular meshwork (TM) cells and human retinal pigment epithelium (ARPE-19) cells following exposure to mechanical strain and oxidative stress.
Authors: Dammak A, Iqbal S, Rao VR, Carracedo G, Kaja S
Purpose: The pathophysiology of glaucoma is multifactorial; however, oxidative stress and biomechanical stress are considered crucial for the initiation of fibrotic changes in the anterior segment and neurodegeneration of the retina and optic nerve. The purpose of this Study was to quantify clinically-relevant biomarkers associated with disease pathology.
A B S T R A C T
Recombinant human PRG4 reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine release from corneal epithelial cells after endotoxin and poly(I:C) insults.
Authors: De Alba M, Iqbal S, Pasupuleti B, Ghosh AK, Sagalov A, Hariani H N, Fareed J, Rao VR, Bacellar-Galdino M, Kaja S
Purpose: In addition to its role in joint lubrication, proteoglycan 4 (PRG4; lubricin) has been shown to be produced by the tear-secreting tissues of the eye, where it protects the cornea and conjunctiva against the shearing forces associated with blinking. Furthermore, recombinant human proteoglycan 4 (rhPRG4) is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of moderate dry eye. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects on rhPRG4 on pro-inflammatory cytokine release from human corneal epithelial cells after endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide, LPS) and poly(I:C) insult.
A B S T R A C T
Inhibition of neutrophil activation by pooled human immune globulins.
Authors: Rao VR, Iqbal S, Ghosh AK, Mun C, Jain S, Bacellar-Galdino M, Kaja S
Purpose: We have previously reported the presence of anti-citrullinated protein autoantibodies (ACPA)targeting histone 4 R3 (H4R3), activated neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in ocular surface washings of patients affected with autoimmune DED. Topically delivered pooled human immunoglobulins (OSIG) were effective in resolving DED signs and symptoms in patients as well as attenuating H4R3 ACPA-induced pathology in mice. Here we extended previous studies evaluating pharmacologic efficacy of OSIG against neutrophil activation in vitro.
Meet with us in New Orleans
Whether you have a question about our science, preclinical models, capabilities, pricing or anything else, our senior management and business development team is ready to answer your inquiries.

Giedrius Kalesnykas, PhD
President and Chief Executive Officer
Dr. Kalesnykas has extensive research experience in eye research and neuroscience developing neuronal-based projects at the University of Eastern Finland and The Wilmer Eye Institute, The Johns Hopkins University, MD, USA. For more info visit Giedrius’ profile page or LinkedIn.

Guillaume Demarne, PharmD
Chief Business Officer
Dr. Demarne has been leading and involved in pharmaceutical operations, fundraising, licensing, and business development for 15 years at international research institutes, biotech start-ups, and pharmaceutical companies in Europe, the U.S., and China. For more info visit Guillaume’s profile page or LinkedIn.

Jenni J. Hakkarainen, PhD
Chief Operating Officer
Dr. Hakkarainen has a strong research background in ex vivo and in vitro drug permeability testing and prediction of drug transport across biological barriers, such as cornea, blood-brain barrier, intestine, and skin. For more info visit Jenni’s profile page or LinkedIn.

Jeff Jamison, PhD
Chief Development Officer
Dr. Jamison is an ophthalmic researcher with degrees in Electrical and Biomedical Engineering. He worked at Pfizer and Alcon before founding Ophthy-DS, a preclinical CRO specializing in ocular toxicology and disease modeling acquired by Experimentica in 2020. More info on Jeff’s profile page or LinkedIn.

Marc Cerrada-Gimenez, PhD
Chief Technology Officer
Dr. Cerrada-Gimenez is an accomplished scientist with extensive experience in in vitro and in vivo modeling in Ophthalmology and neurodegeneration. He manages the development and implementation of innovative technologies to optimize Experimentica’s preclinical research capabilities. For more info visit Marc’s profile page or LinkedIn.