Summary: The rodent blue light damage (BLD) model is a well-established model for retinal degeneration, oxidative stress and neuroinflammatory activity.
Model description
Blue Light Damage (BLD) is a multi-faceted process affecting chromophores that absorb blue light, such as cytochrome oxidase and rhodopsin. The BLD model is a quick inducible method for causing photo-oxidative damage that is primarily localized to the outer retina, including bipolar, photoreceptor and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cell layers. Because cell death is apoptotic rather than necrotic, the BLD model mirrors retinal degeneration in human diseases including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), and retinal detachment. Acute BLD typically results in geographically irregular apoptosis and retinal atrophy, which is similar to atrophy seen in the terminal stage of dry AMD.
At Experimentica, we have fully implemented and validated the rat BLD model with clinically relevant reference compounds and the most comprehensive list of read-outs.
| Animal species | Rats |
| Method of induction | Blue light |
| Follow-up period | Typically up to 7 days |
| Route of compound administration | Intravitreal, topical, systemic |
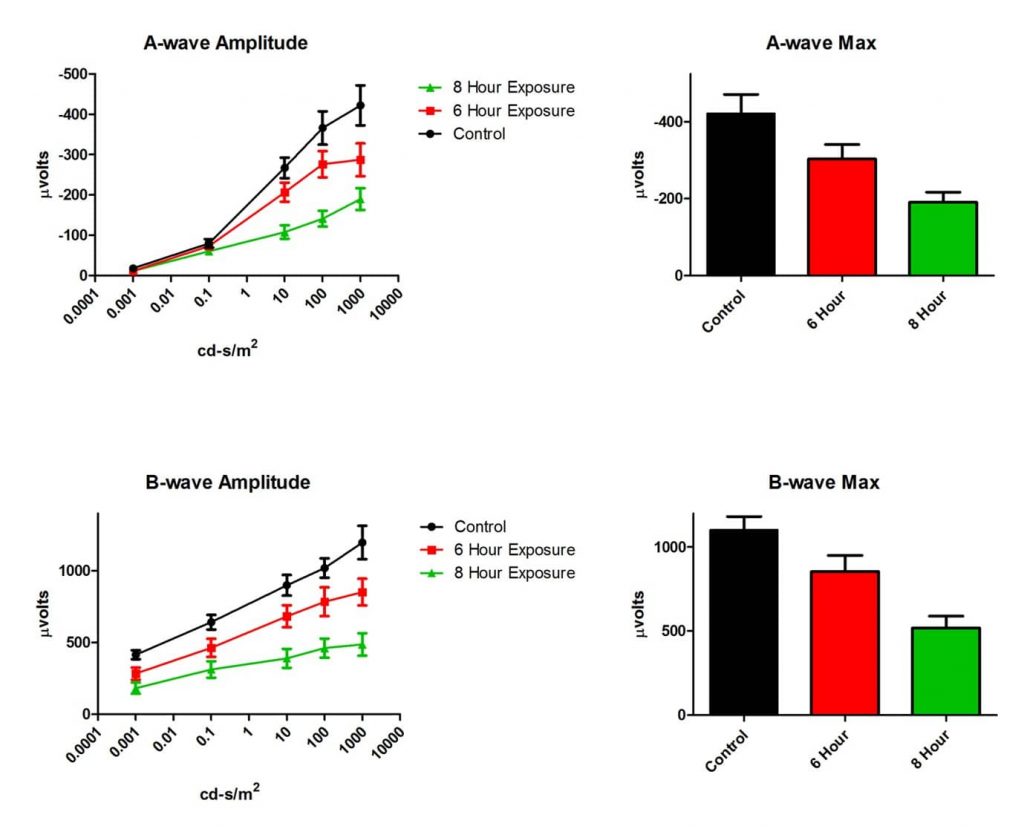
| Read-outs | 1. Flash electroretinography (fERG): functional deficits are observed both in a-wave and b-wave amplitudes in 6- and 8-hour exposure to blue light; 2. Histology: quantitative assessment of retinal thickness |
Outcomes and Capabilities
Functional assessment
We use flash electroretinography (fERG) to observe functional deficits both in a-wave and b-wave amplitudes in 6 and 8 hour exposure to blue light in the rat BLD model.
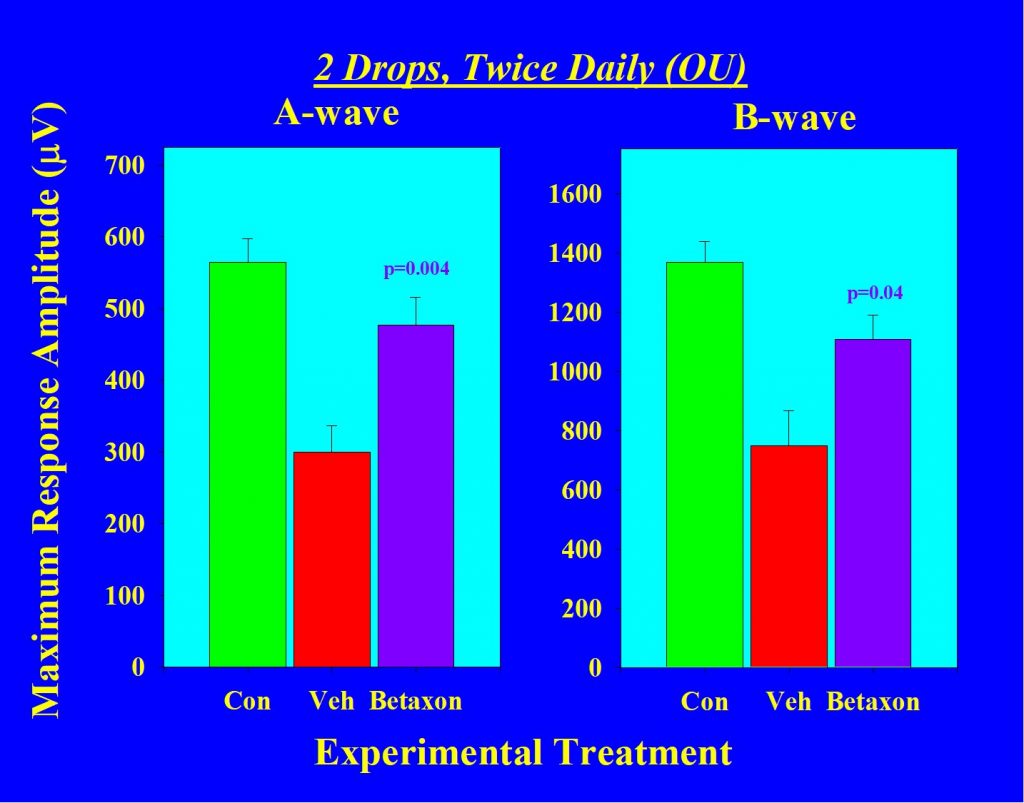
We also use flash electroretinography (fERG) to observe functional deficits both in a-wave and b-wave amplitudes in vehicle treated eyes compared to Betaxon treated eyes.
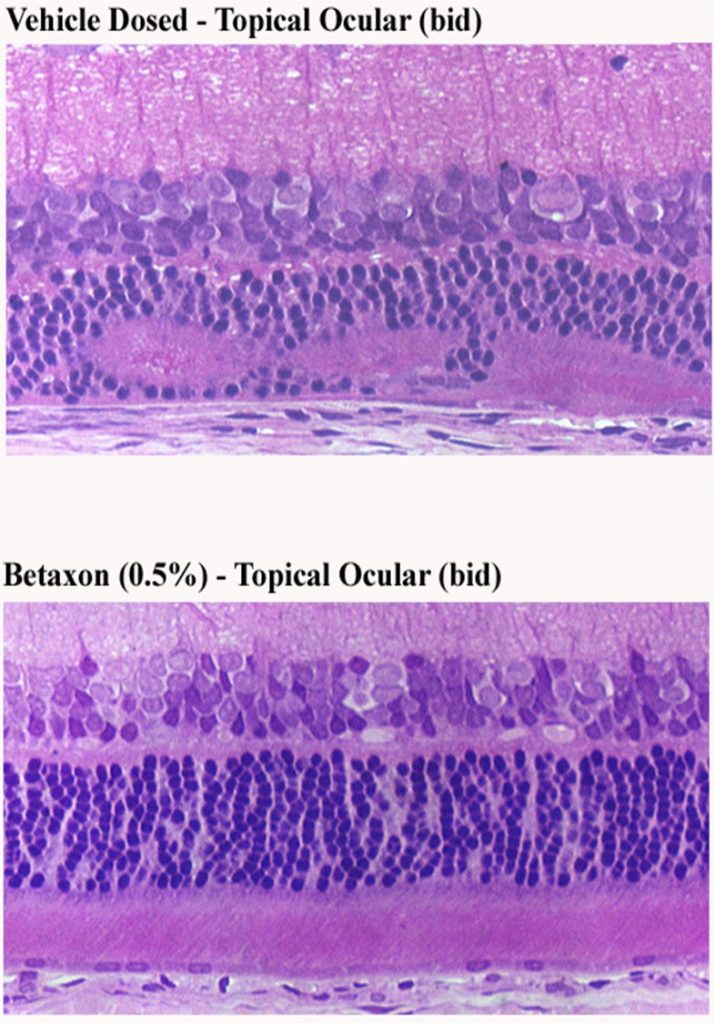
Histology
Retinal histologic sections showing protection of retina in Betaxon treated eye on a rat BLD model.
References
- Jamison J, Vihtelic T. Blue Light Damage Susceptibility of Albino And Pigmented Rats Strains. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011; 52(14):1849.
- Linton E, Wang C, Song D, Zhao L, Song Y, Jamison J, Freshley J, Zacks D, Dunaief J. Role of the Fas death receptor in light-damage induced photoreceptor degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.. 2016; 57(12):5797.



